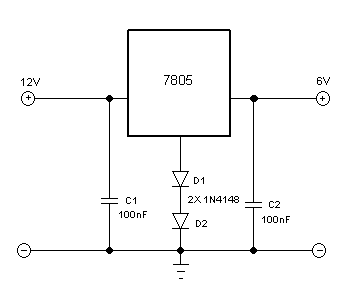
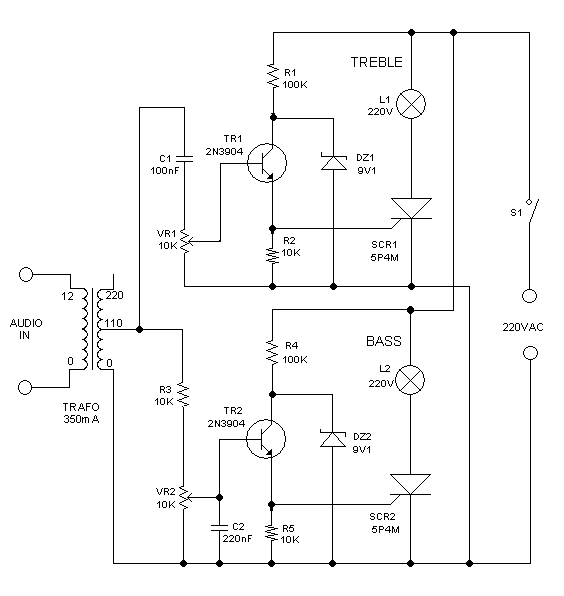
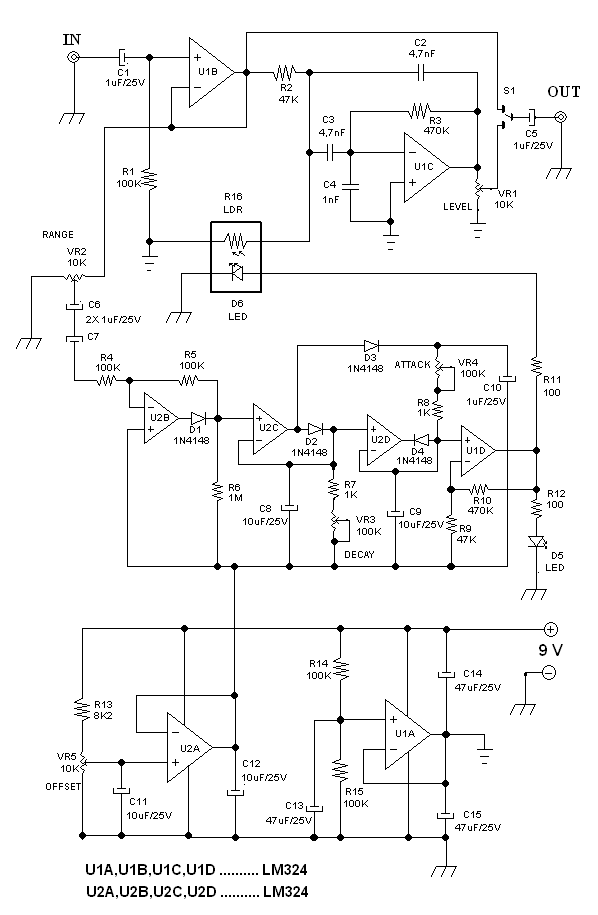
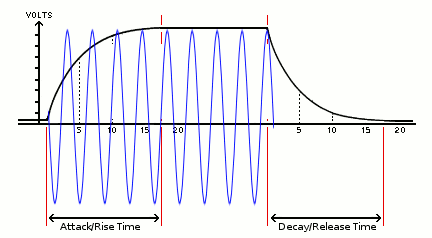
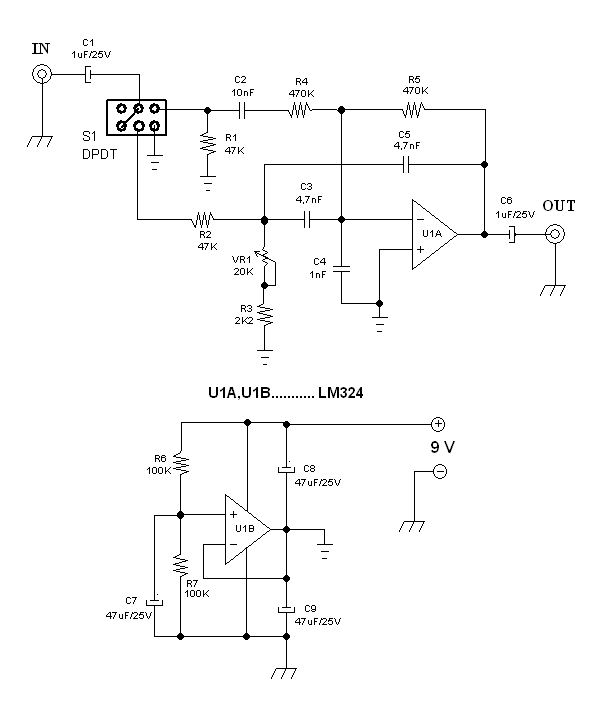
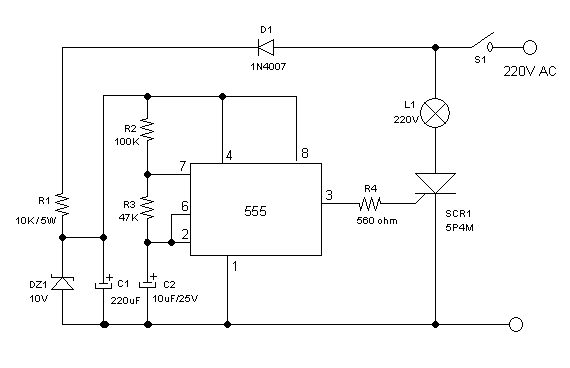
Arduino HM-936D Soldering Station Controller Development
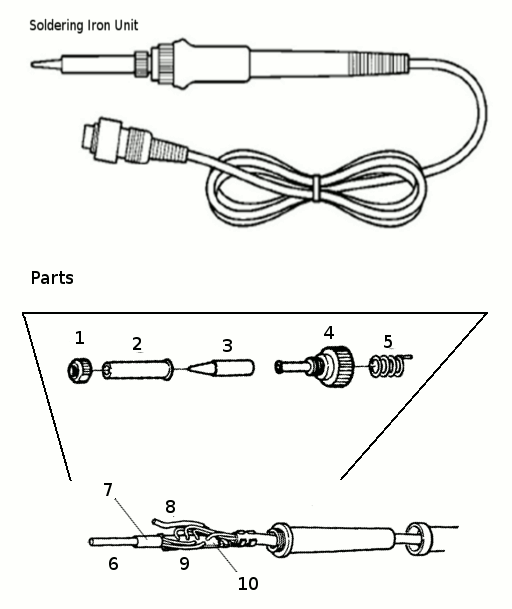
A. Introduction: The 936 Soldering Station Series in The Market With the popularity of specific brand’s soldering station labeled with 936-series, many manufacturers (mostly Chinese companies) make benefits by producing the counterfeit products with the generic names “936 series” soldering station. It is a good things that their parts are widely available on the online marketplace, as shown in the […]
Read more